
Case Study
Allosteric Drug Development —
Revealing the Mechanismof the Aryl
Hydrocarbon Receptor (AHR)
Highlights
The molecular mechanism of the allosteric agonist was revealed and the patent application Strategy for this compound was determined within 4 months.
Project Overview
Client
Listed Biotech Company
Objective
Activation Mechanism of the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor (AHR) (Classical Signaling Pathway)
Main Challenge
The activation mechanism of the agonist is unknown; only the cryo-EM structure of the agonist-bound complex is available, lacking the structure in the ligand-free (apo) state; no published studies have clarified the relevant activation mechanism.
Design Strategy /
Approach
Approach
Divamics conducted multi-scale molecular dynamics simulations on the entire receptor complex to study the agonist binding-induced conformational changes, guiding the optimization of agonist potency.
Key Results /
Milestones
Milestones
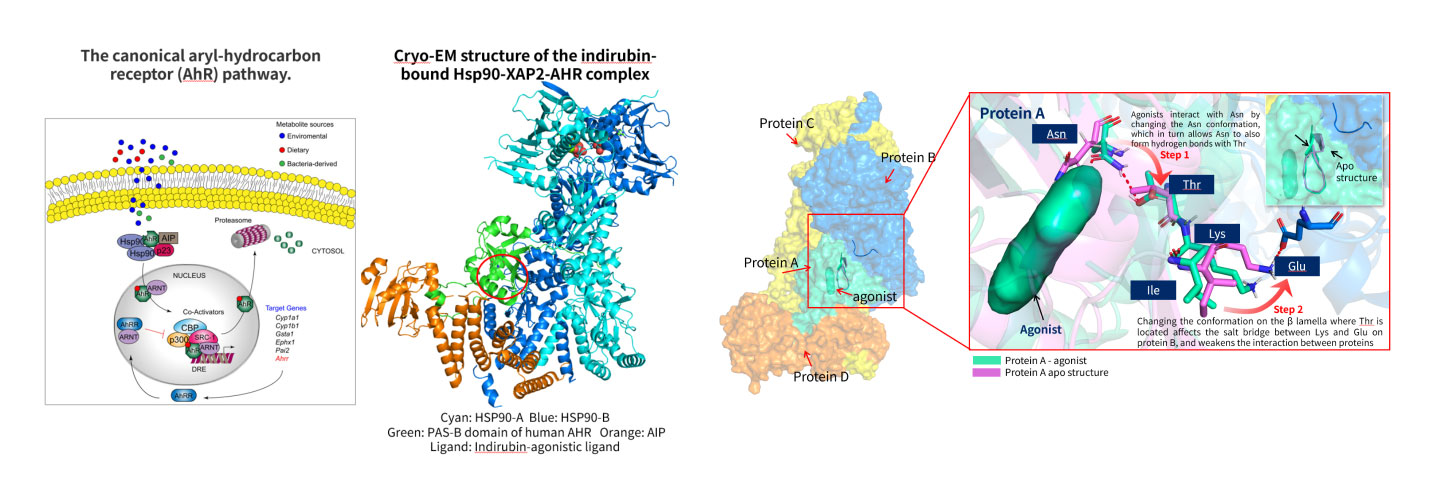
- MD simulations revealed the value of Molecular Dynamics: Through long-term dynamics simulations of tens of microseconds, it was found that the binding of the agonist to the allosteric site can trigger a cascade of pushing conformational changes between the side chains of key residues, ultimately leading to weakened protein-protein interactions.
- Core of Allosteric Design:
1. the agonist interacts with asparagine (Asn) by altering its conformation, thereby promoting the formation of a hydrogen bond between Asn and threonine (Thr).
2. Alter the conformation of the β-sheet where Thr is located, affecting the salt bridge between lysine (Lys) and glutamic acid (Glu) on Protein B, so to weaken protein-protein interactions
Interested in how Divamics can accelerate
your next discovery project?
Contact Us

